Blockchain Merges Into A Carbon-Neutral World
October 1, 2022
Blockchain Merges Into A Carbon-Neutral World
The world’s second largest cryptocurrency goes carbon neutral, iron and steel industries spend a cool $250 billion to reach net-zero, and one company turns seaweed into carbon credits.
All that and more in this week’s carbon news.
Here we go!
Ethereum: Merge Now For Carbon-Friendly Blockchains
Ethereum, the second-largest blockchain, is the base layer for a number of crypto applications and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) protocols. Now, the entire Ethereum ecosystem is almost completely carbon-neutral, thanks to The Merge.
The Merge was the name for Ethereum’s long-planned upgrade from an energy-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to a less-intensive Proof-of-Stake system. Early estimates indicate that the Ethereum Merge reduced carbon emissions from the network by over 99%. So much for that objection; will this be the catalyst for much broader crypto adoption?
Iron and Steel Pays Up
Emissions-heavy industries like steel and iron manufacture pose a special challenge for net-zero goals. There’s no easy way to reduce emissions, which makes offsets particularly inviting.
That’s probably why a recent analysis says that the iron and steel industry will need to pony up a cool $1.4 trillion to decarbonize - and $250 billion of that will go towards carbon offsets. The complete plan requires a total rethink of the industry, for how and where the ore is mined to new processing methods. Carbon offsets will grease the wheels on the entire process.
Who Loves Seaweed Now?
Seaweed - particularly the sargassum variety that blankets much of the Atlantic each year - isn’t the most glamorous plant. In fact, it can be downright hazardous, clogging beaches, harming wildlife, and emitting methane when it dies back.
Now one company, Carbonwave, is trying to turn that negative into a positive. Carbonwave harvests the sargassum during the annual blooms and turns it into everything from emulsifiers to bio-leathers. Sargassum is a carbon sink while it grows; by processing it into something commercially useful, Carbonwve can create legitimate carbon offsets.
It’s a great tool against climate change, and one more example of the dramatic co-benefits high-quality carbon offsets bring.
Ammonia - The Unsung Hero of Green Hydrogen
1 billion tonnes of CO2 emissions per year. That’s the shipping industry’s current tally - and it ain’t pretty.
The clock is ticking to reduce that amount fast, but those big boats are crucial to the world’s economy - and they don’t run on nothing. Long-term, there’s a big push for clean hydrogen, but the infrastructure for that transition will take years to develop.
In the meantime, there’s ammonia.
Ammonia is already a viable fuel, and as a vital part of the agricultural economy there’s plenty of existing infrastructure. Add that all up, and ammonia could potentially serve as a bridge between existing fossil fuels and clean hydrogen.
Even with markets around the world experiencing significant turmoil, the net-zero push shows no sign of letting up. The global carbon markets, including the VCM, are going absolutely nowhere - and their importance will only grow.
Carbon Fact of the Week
Slowing down. To date, that has been the single biggest tool in the shipping industry’s toolbox to reduce CO2 emissions. That’s important, because the shipping industry accounts for some 80% of the world’s transportation CO2e.
300 million barrels per day. That’s how much oil is burned, per day, by the shipping industry; roughly 5% of total world production.
And now, the big boats can’t slow down any more without stressing the global supply chain. That makes alternative fuels a must-have, putting renewed pressure on the race to find alternatives like hydrogen.
Source: https://carboncredits.com/


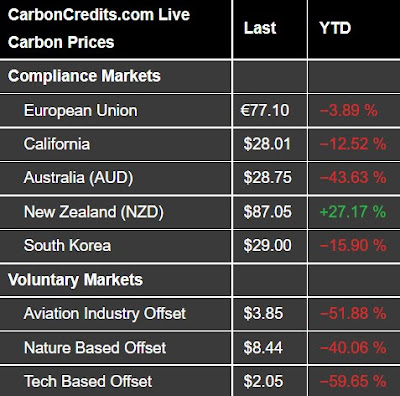
.jpg)
.jpg)
댓글
댓글 쓰기